Did you know that the human body primarily comprises water, with roughly 60% of our composition being H2O? It’s no wonder that staying hydrated is so critical for maintaining good health! But did you also know that dehydration could potentially cause back pain? How can dehydration cause back pain?
When we become dehydrated, our bodies lose more fluids than they take in, which can lead to various symptoms, such as fatigue, dizziness, and muscle cramps. In severe cases, dehydration can cause muscle spasms in the back, leading to pain and discomfort.
The spinal discs need water to cushion your spine from the impact of your movements. Dehydration makes them lose water and become stiff, which causes back pain.
How can dehydration cause back pain?
A CDC report says that over a third of US adults don’t drink enough water daily. This can dehydrate them, harming their health in many ways.
Dehydration can cause back pain in several ways. When we don’t drink enough water, our bodies lose fluids, which can lower our blood volume and the amount of nutrients and oxygen that reach our muscles. This can make our muscles cramp and spasm, hurting and affecting the back muscles.
To know how dehydration leads to back pain, you must know how your spine is built and why fluid is vital for the system.
The spine is made up of small bones called vertebrae that are stacked on top of each other. Between each vertebra is a fluid-filled disc that acts as a cushion. The spine protects the spinal cord and spinal nerves that run through the center of the spine.
The fluid in the spine, called cerebrospinal fluid, serves several essential functions:
- It cushions and protects the spine. The fluid-filled discs between the vertebrae act as shock absorbers and prevent the vertebrae from grinding against each other. This helps reduce friction and prevents damage to the spine.
- It nourishes the spine. The cerebrospinal fluid delivers nutrients to the spine and removes waste products. The discs and vertebrae contain no blood vessels, so they rely on the fluid to provide nutrition and remove waste.
- It protects the spinal cord and nerves. The cerebrospinal fluid surrounds the spinal cord and nerves, protecting them from damage and injury.
- It allows the spinal cord and nerves to move freely. The cerebrospinal fluid allows the spinal cord and nerves to move within the vertebral column as our body moves. Without this fluid cushion, the spinal cord and nerves would be compressed during movement.
- It maintains even pressure around the brain and spine. The cerebrospinal fluid maintains a consistent pressure around the brain and spine, which helps to protect them from sudden impacts and changes in pressure.
Dehydration can exacerbate back problems, such as herniated discs, by reducing the cushioning effect of spinal discs and increasing pressure on the spine. This can result in pain and discomfort in the back, particularly in the lower back.
What does dehydration and back pain feel like?
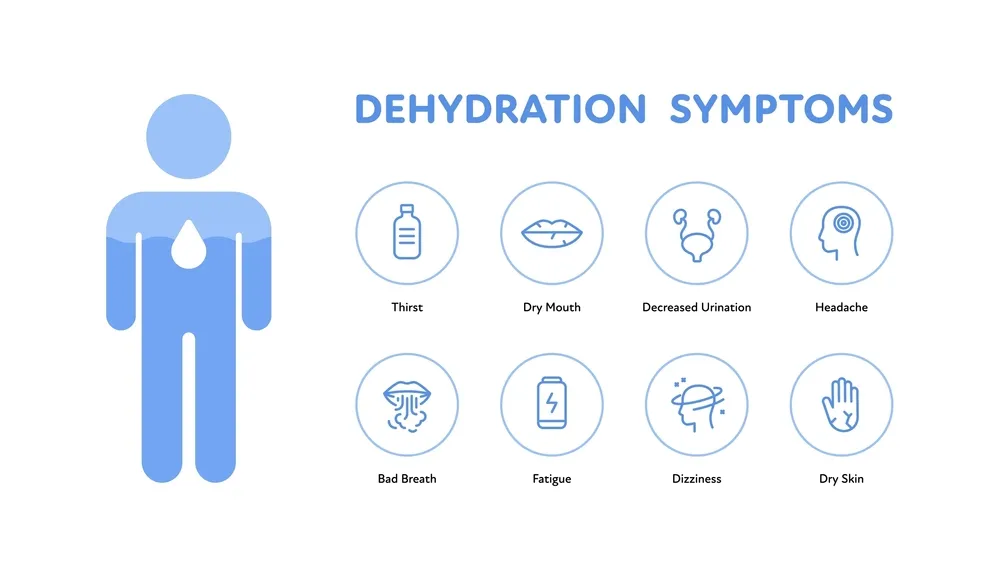
Dehydration and back pain can cause various symptoms that vary in severity and location depending on the individual.
If you are dehydrated, you may experience symptoms such as:
- Thirst
- Dry mouth and throat
- Fatigue or weakness
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Headache
- Dark yellow urine
- Dry skin
- Bad breath
If you are experiencing back pain due to dehydration, you may also feel:
- Muscle cramps or spasms in the back
- Stiffness or soreness in the back muscles
- Shooting or stabbing pain in the lower back
- Reduced range of motion in the back
- Pain that worsens with movement or activity
How to avoid back pain from dehydration
Staying well hydrated by drinking enough fluids throughout the day is essential to prevent back pain from dehydration. Here are some tips to help you stay hydrated and avoid back pain:
Drink water often
Aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water daily if you are active or in a hot environment. You can also drink other fluids, such as sports drinks, herbal tea, or coconut water, to help restore lost fluids.
Eat foods with a lot of water
Fruits and vegetables such as watermelon, cucumber, and celery are rich in water and can help keep you hydrated.
Avoid sweet and caffeinated drinks
These can have a diuretic effect and may make you more dehydrated.
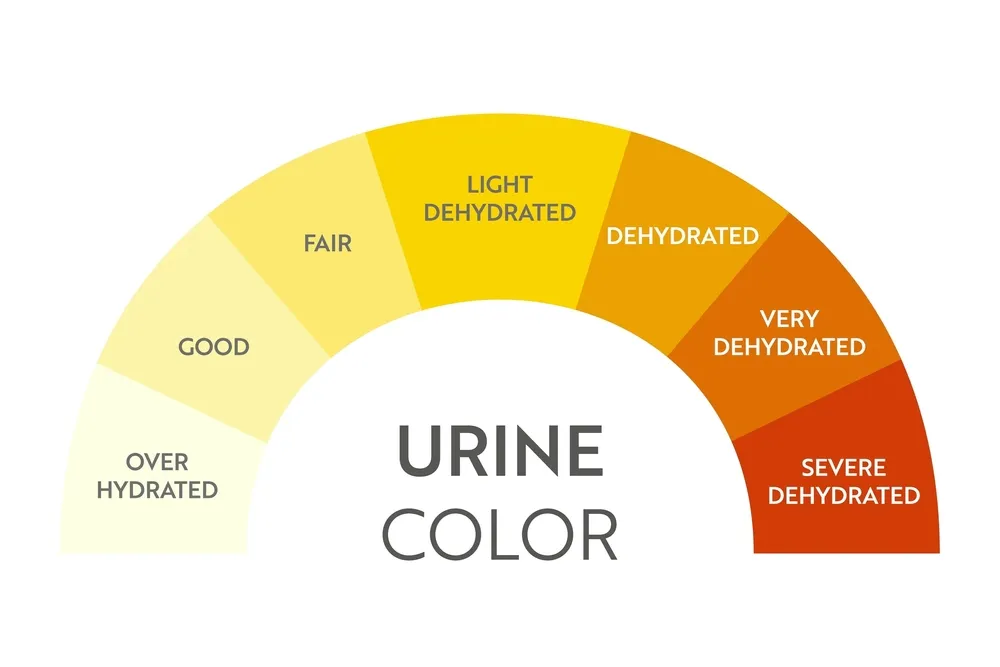
Check your urine color
If your urine is dark yellow, it may be a sign that you are dehydrated. Aim for a light yellow color as a sign of good hydration.
Take breaks and stretch
If you have a job requiring you to sit for long periods, take breaks to stand up and stretch your back muscles. This can help prevent muscle tightness and pain.
Avoid overdoing it
If you are active, take breaks and drink plenty of fluids during and after exercise to prevent dehydration and back pain.
By following these tips, you can help prevent dehydration and the back pain that can go with it.
FAQs
Conclusion
Dehydration can also lead to kidney problems, such as kidney stones, which can cause intense back pain. When the kidneys are dehydrated, they may not work well, accumulating waste products and minerals in the kidneys that can form stones. These stones can hurt as they move through the urinary tract, including the back.
In particular, the nucleus pulposus, which is the jelly-like substance in the middle of each spinal disc, can be affected by dehydration. When the body is dehydrated, the nucleus pulposus can lose moisture, becoming less able to pad the spine, leading to more pressure on nearby nerves and tissues. This can cause back pain, especially in the lower back.

