
A 12-year-old boy in Maryland died tragically about 15 years ago. His death made national headlines because an untreated tooth infection caused it. His case shows a severe warning: Dental issues can be deadly, even though they are rare. Keep reading to find out can a cavity kill you. You will also learn some simple things you can do to protect yourself.
A cavity may not seem like a big deal, but it can seriously affect your dental and overall health. When you don’t take good care of your teeth and gums, you may develop other dental issues, such as gum disease, tooth loss, and jawbone damage.
Sometimes, a cavity can also cause a dental abscess, a dangerous infection that can spread to other body parts. If the infection reaches the bloodstream, it can trigger sepsis, a deadly condition that can harm multiple organs and potentially cause death.
How can a cavity kill you
A cavity is usually considered a minor nuisance—a small hole in a tooth that requires a filling. However, if left untreated, a cavity can become a dangerous and even life-threatening condition. Here’s how:
An untreated cavity will grow larger and deeper over time as bacteria erode enamel and dentin. Eventually, the decay can reach the tooth’s nerve center, causing severe toothache and infection. The infection can then spread beyond the tooth into the jawbone and other surrounding tissues. This is known as an abscess, and the swelling can spread throughout the face and neck.
In rare cases, the infection can enter the bloodstream, causing a dangerous condition known as sepsis. As the bloodborne bacteria circulate through the body, they release toxins that can cause a cascade of life-threatening complications like organ failure, loss of limbs, or even death. This is rare, but it is possible—so while that tiny hole in your tooth may seem harmless, it’s best not to ignore it for long.
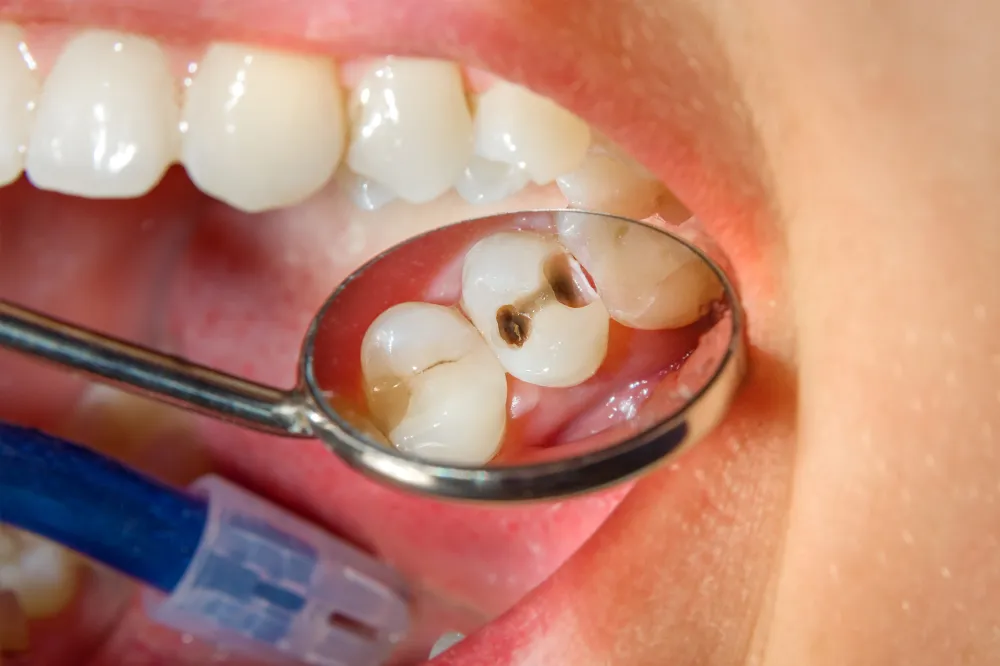
Life-threatening problems that can arise due to an untreated tooth infection
Untreated tooth infections can lead to several life-threatening problems. Here are a few examples:
Dental abscess
A dental abscess is one of the most common infections from an untreated cavity. This painful infection usually happens at the root of the tooth or between the tooth and the gum. An abscess can cause swelling, redness, and pus-filled pockets around the affected tooth. It can also cause fever, swollen lymph nodes, and general feelings of sickness.
Sepsis
A severe tooth infection can cause bacteria to enter the bloodstream, leading to sepsis. This is a potentially life-threatening condition in which the body’s immune system goes into overdrive, leading to widespread inflammation and organ damage.
Ludwig’s angina
This is a rare but serious bacterial infection that can occur when a tooth infection spreads to the soft tissues of the neck and face. It can cause swelling and inflammation that can obstruct the airway, leading to difficulty breathing and potentially suffocation.
Cavernous sinus thrombosis
This is a rare but severe complication that can occur when a tooth infection spreads to the veins in the brain. It can cause a blood clot in the cavernous sinus, a cavity at the base of the brain. This can lead to swelling and pressure in the brain, potentially causing seizures, paralysis, and even death.
Brain abscess
A tooth infection that spreads to the brain can cause a brain abscess, a collection of pus that can cause swelling and pressure in the brain. This can lead to headaches, seizures, and neurological problems and can be life-threatening if not promptly treated.
How to protect yourself
Tooth infections used to be fatal 10 – 40% of the time in the early part of the 20th century. Luckily, those numbers are much lower now. You can almost eliminate your risk of dying from a dental problem if you take some simple steps, such as:
Practice good oral hygiene
Brush your teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, floss daily, and use an antiseptic mouthwash to help remove plaque and bacteria from your teeth and gums.
Limit sugary foods
Sugary and acidic foods and drinks can contribute to tooth decay and erosion, increasing the risk of tooth infections. Limit your consumption of sugary and acidic foods and drinks, and drink plenty of water to help wash away food particles and bacteria.
Visit your dentist regularly
Regular dental checkups and cleanings can help detect and treat tooth decay and other dental problems before they progress, potentially leading to infections.
Don’t ignore signs of infection
If you experience severe tooth pain, swelling, fever, difficulty swallowing, or breathing, seek emergency dental or medical care immediately. These can be signs of a severe dental infection that requires immediate treatment.
By taking these steps, you can help protect yourself from tooth infections and maintain good dental and overall health.

What are some treatment options for cavities?
The treatment options for cavities can vary depending on the severity of the cavity. Here are some common treatment options:
Dental fillings
This is the most common treatment for cavities. The dentist will remove the decayed portion of the tooth and fill the cavity with a tooth-colored filling material.
Crowns
If the cavity is too large for a filling, a crown may be necessary. A crown is a cap that covers the entire tooth and restores its shape and strength.
Root canal therapy
If the cavity has reached the pulp of the tooth, a root canal may be necessary. During this procedure, the dentist will remove the infected or damaged pulp and replace it with a filling material.
Extraction
If the cavity is too extensive and the tooth cannot be saved, the dentist may recommend removing the tooth.
FAQs
Conclusion
To sum up, a teeth cavity itself is not usually deadly, but it’s crucial not to overlook the potential dangers of neglecting your dental health.
Untreated cavities can cause serious dental problems such as gum disease, tooth loss, and dental abscesses, which can cause pain and discomfort and affect your quality of life.
In some rare cases, an untreated dental infection can spread to other parts of the body and cause life-threatening complications such as sepsis, Ludwig’s angina, or brain abscesses.
To protect yourself from tooth infections, it’s essential to practice good oral hygiene, limit sugary and acidic foods and drinks, see your dentist regularly, treat dental problems quickly, and seek emergency dental or medical care if you experience signs of infection.

